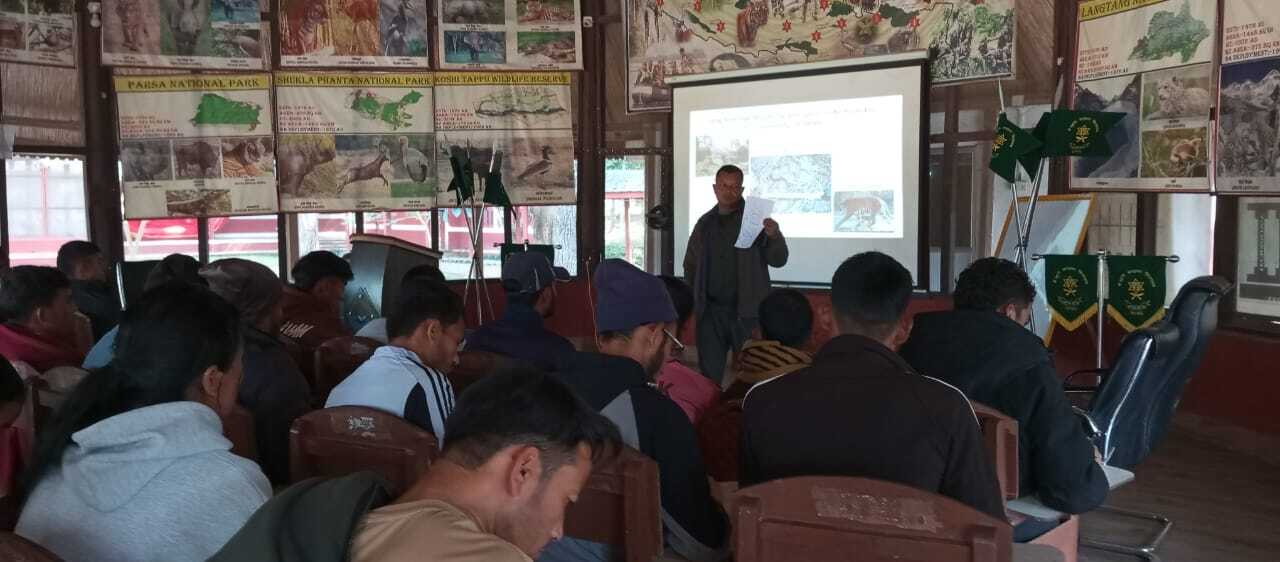

Nepal Tiger Trust (NTT) technicians play a crucial role in training the next generation of field staff. On December 29, 2024, Chitwan Park warden Mr. Divesh Shrestha invited our technicians as instructors for training new game scouts. Our senior technicians, Mr. Baburam Mahato and Mr. Raju Kumal, provided information on basic tiger behavior and tracking techniques to nearly 50 trainees.
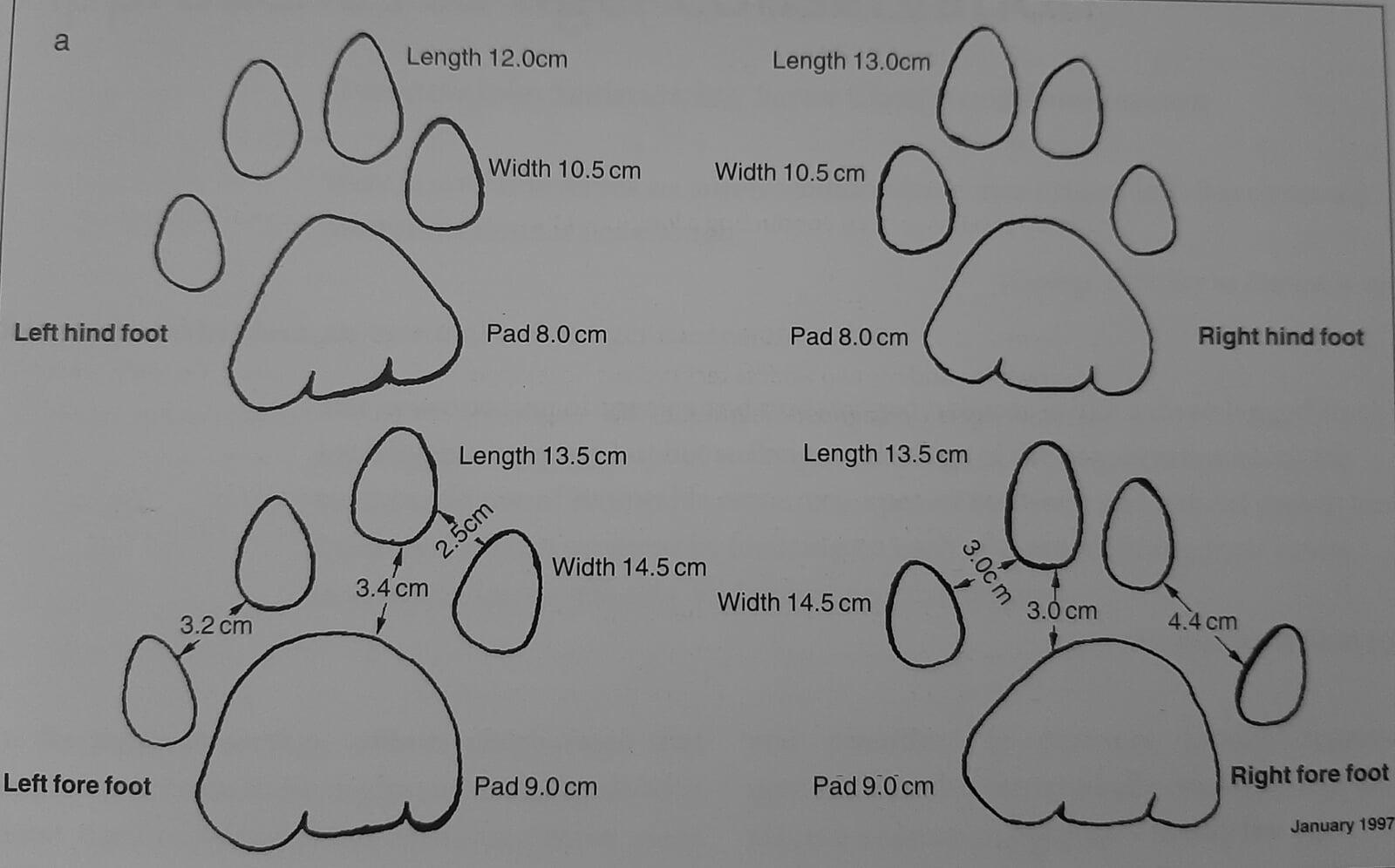
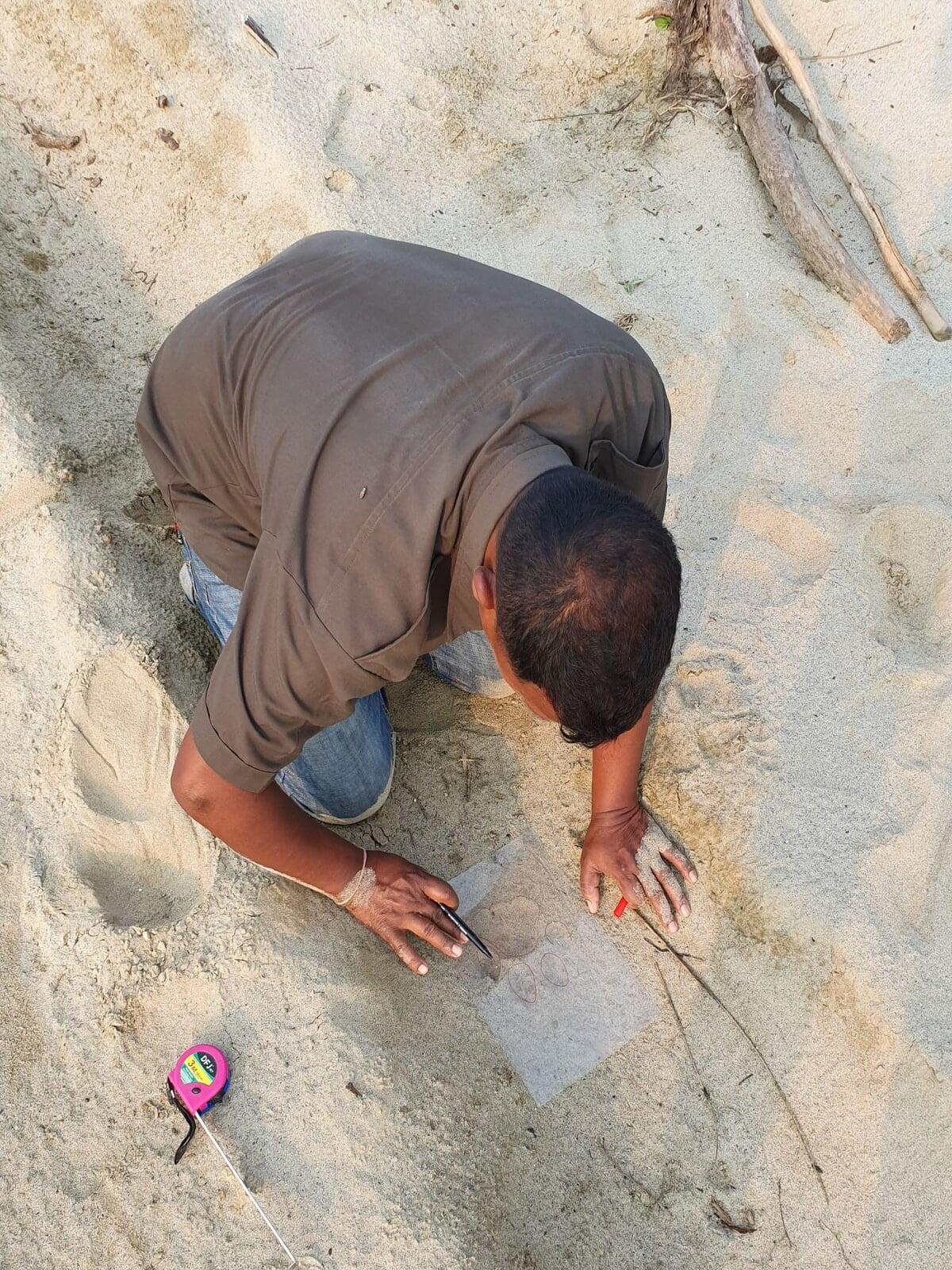
- Pugmark Tracking: This traditional method involves identifying and measuring the footprints (pugmarks) of tigers. It requires knowledge of the tiger's foot anatomy and careful measurement of the tracks to identify the tiger and determine its direction of movement.
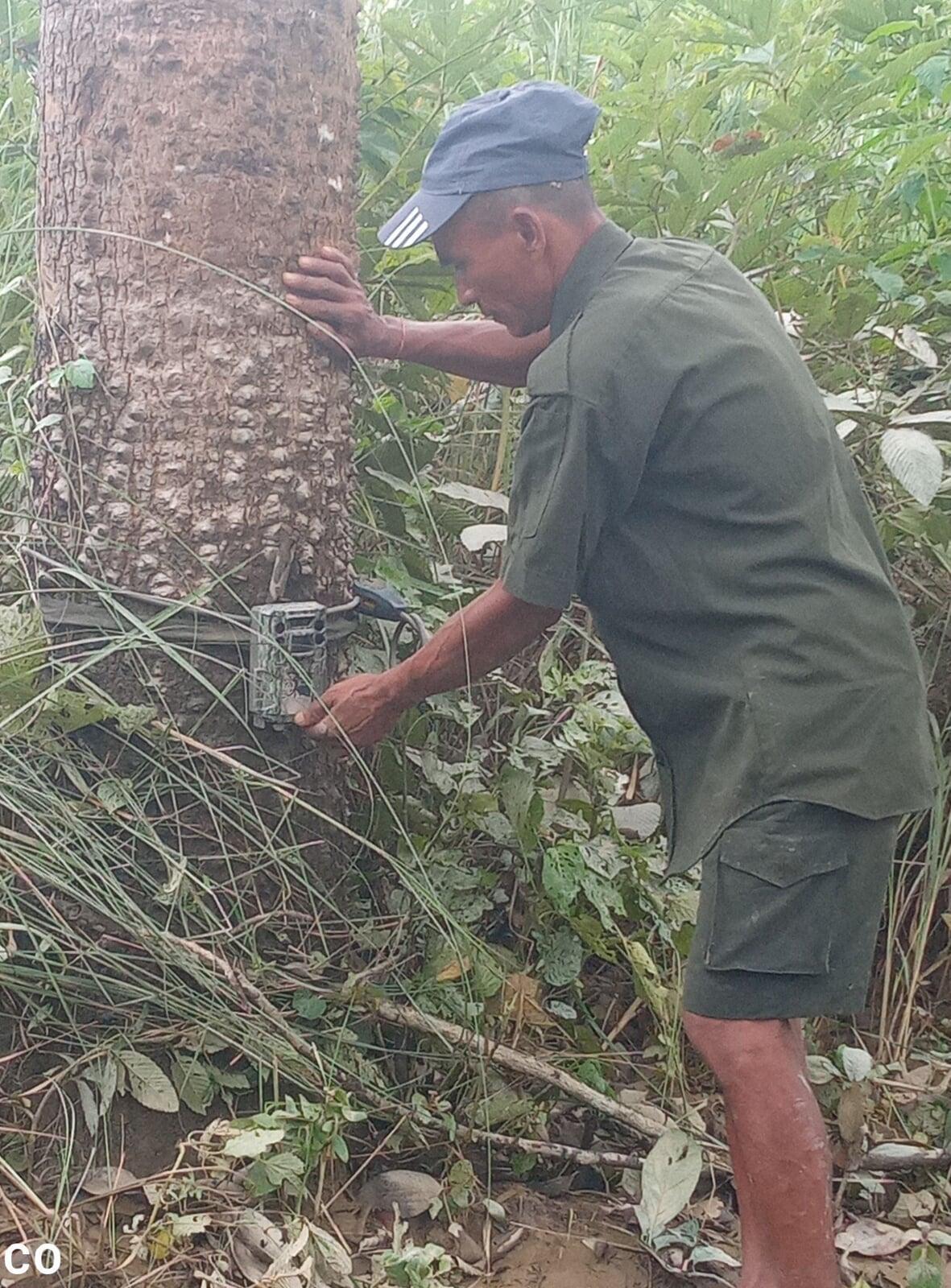
- Camera Traps: These motion-activated cameras are placed in strategic locations within tiger habitats. Camera traps capture images or videos of tigers as they pass by, providing valuable data on tiger presence, population estimates, and individual identification through unique stripe patterns.

- Scat Analysis: Collecting and analyzing tiger scat (feces) helps researchers gather information about the tiger's diet and genetic makeup.
- Acoustic Monitoring: This technique involves recording and analyzing tiger vocalizations, such as roars and growls.
- GPS Collaring: In some cases, researchers fit tigers with GPS collars to track their movements in real-time. This method provides detailed information on tiger home ranges and habitat use.
- Field Signs: Observing field signs such as scratch marks on trees, claw marks, and territorial markings help researchers identify tiger presence and territorial boundaries.

When used together, these techniques provide a comprehensive understanding of tiger behavior, population dynamics, and habitat requirements, aiding in effective conservation efforts. This is how the Nepal Tiger Trust has been collaborating and assisting the park in capacity building of field personnel.
We invite you to support our conservation efforts by donating and sharing this cause. To stay updated with the latest tiger news, please subscribe
